Documentation
About Kubeapps
Tutorials
- Get Started with Kubeapps
- Using an OIDC provider
- Managing Carvel packages
- Managing Flux packages
- Kubeapps on TKG
How-to guides
- Using the dashboard
- Access Control
- Basic Form Support
- Custon App View Support
- Custom Form Component Support
- Multi-cluster Support
- Offline installation
- Private Package Repository
- Syncing Package Repositories
- Using an OIDC provider with Pinniped
Background
Reference
About the project
Get Started with Operators in Kubeapps ¶
This guide will walk you through the process of enabling support for Operators in Kubeapps and deploy an Operator instance.
In this tutorial we will be using the Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) to expose the Operators from the OperatorHub .
Prerequisites ¶
Kubeapps assumes a working Kubernetes cluster (v1.12+) and
kubectl
installed and configured to talk to your Kubernetes cluster. Users following this tutorial require to have admin privileges in the cluster in order to install and manage Operators.
Step 1: Enable Operators support in Kubeapps ¶
Since Kubeapps v2.4.3 (package version 7.8.4), Operators support is deactivated by default.
In order to enable it, set up Kubeapps with the following chart value:
featureFlags:
operators: true
Step 2: Install the Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) ¶
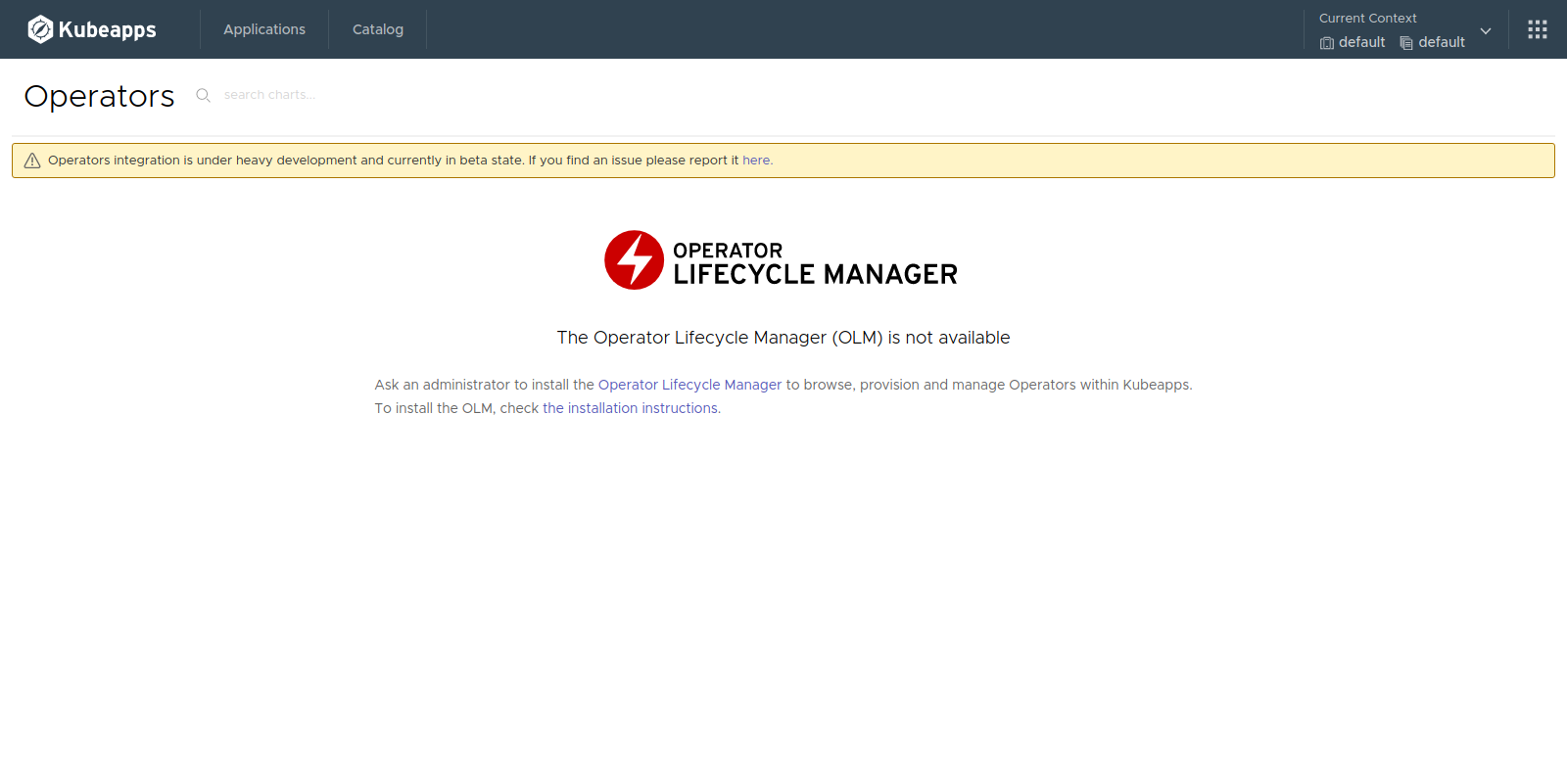
Since Kubeapps 2.0, Operators are available by default. Once you access to the dashboard, if you click on the menu icon and select “Operators”, you will see a message alerting that the OLM is not installed:
Follow the instructions to install the latest OLM version. For example:
curl -L https://github.com/operator-framework/operator-lifecycle-manager/releases/download/v0.20.0/install.sh -o install.sh
chmod +x install.sh
./install.sh v0.20.0
Note that you will need special permissions to manage Operators. If you receive a Forbidden error, apply the following ClusterRole to your admin user:
kubectl create clusterrolebinding kubeapps-operator-cluster-admin --clusterrole=cluster-admin --serviceaccount kubeapps:kubeapps-operator
NOTE: replace the kubeapps:kubeapps-operator with the service account you are using or the cluster user.
Step 3: Install an Operator ¶
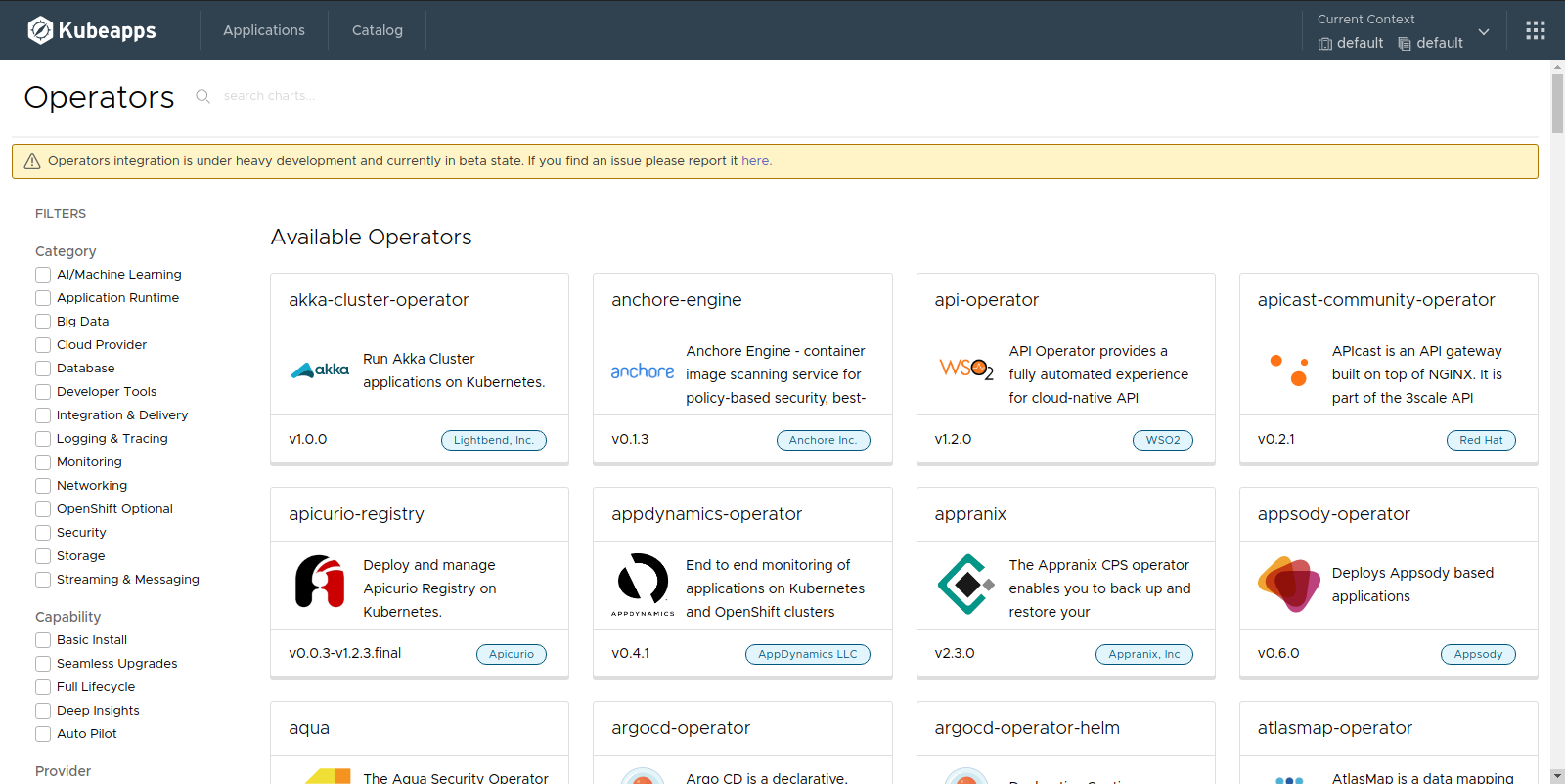
After some minutes, you should be able to see the full list of Operators available:
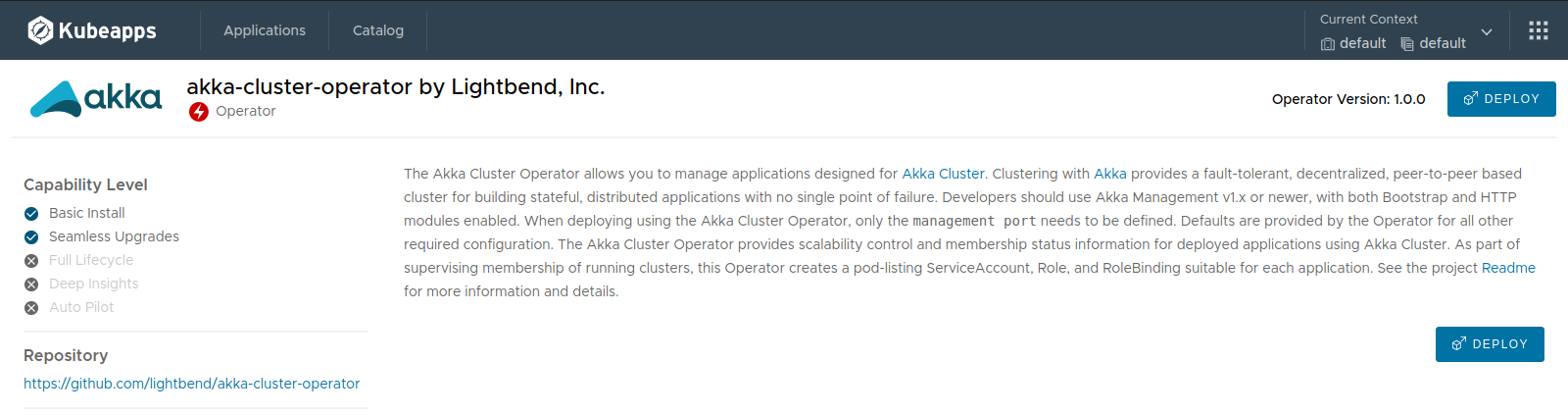
Let’s deploy the “Akka Cluster Operator”. When clicking on it, the information about the Operator is displayed:
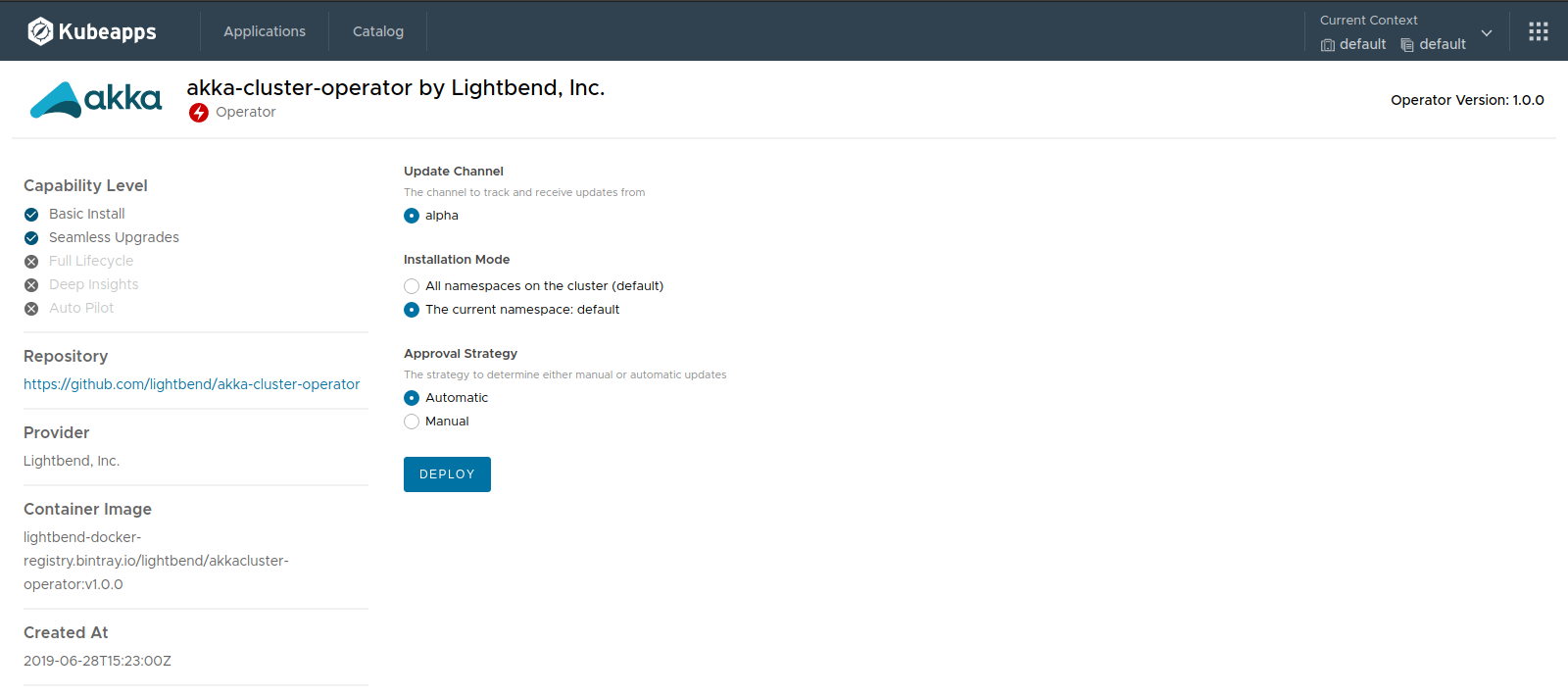
When clicking on the Deploy button, a form to deploy the operator will be displayed. There are two types of Operators: Global and namespaced. Namespaced Operators will be available in a single namespace while global Operators across the cluster. In this case, we are installing a global Operator:
Once the Operator is installed it would be listed like that and after a minute or two, you can start deploy instances of that Operator:
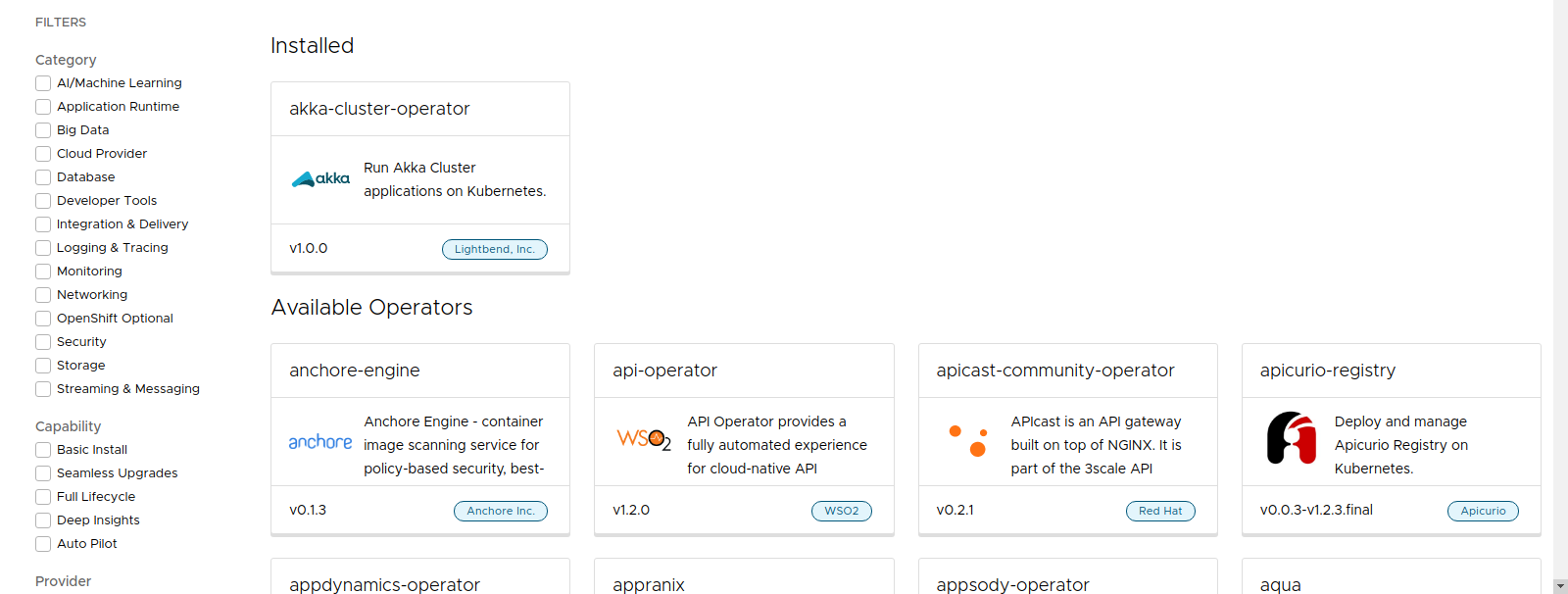
Step 4: Deploy Resources Managed by an Operator ¶
Now, available applications related to an Operator are listed in the Catalog along with the existing Helm Charts:
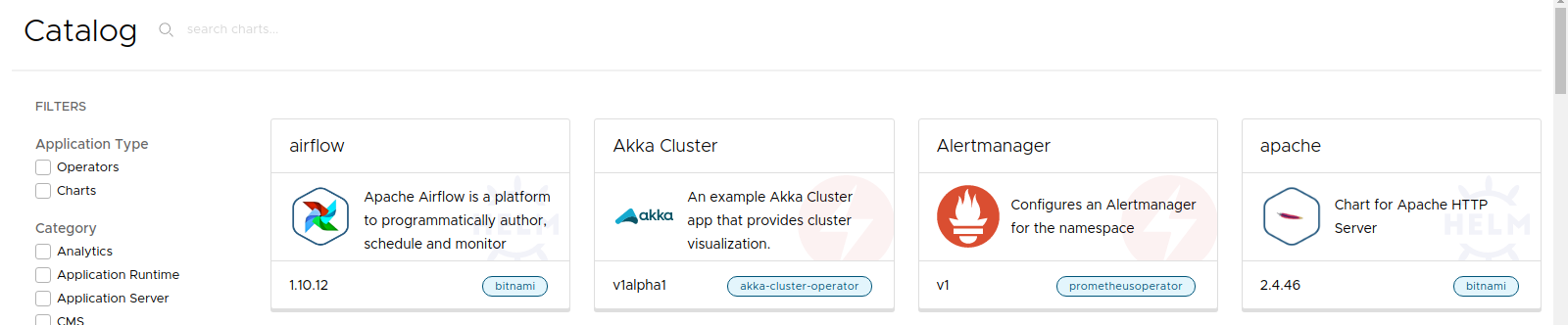
You can filter out Charts and select the Akka Cluster example. That would render the YAML form in which you can modify any setting in order to deploy a custom instance:
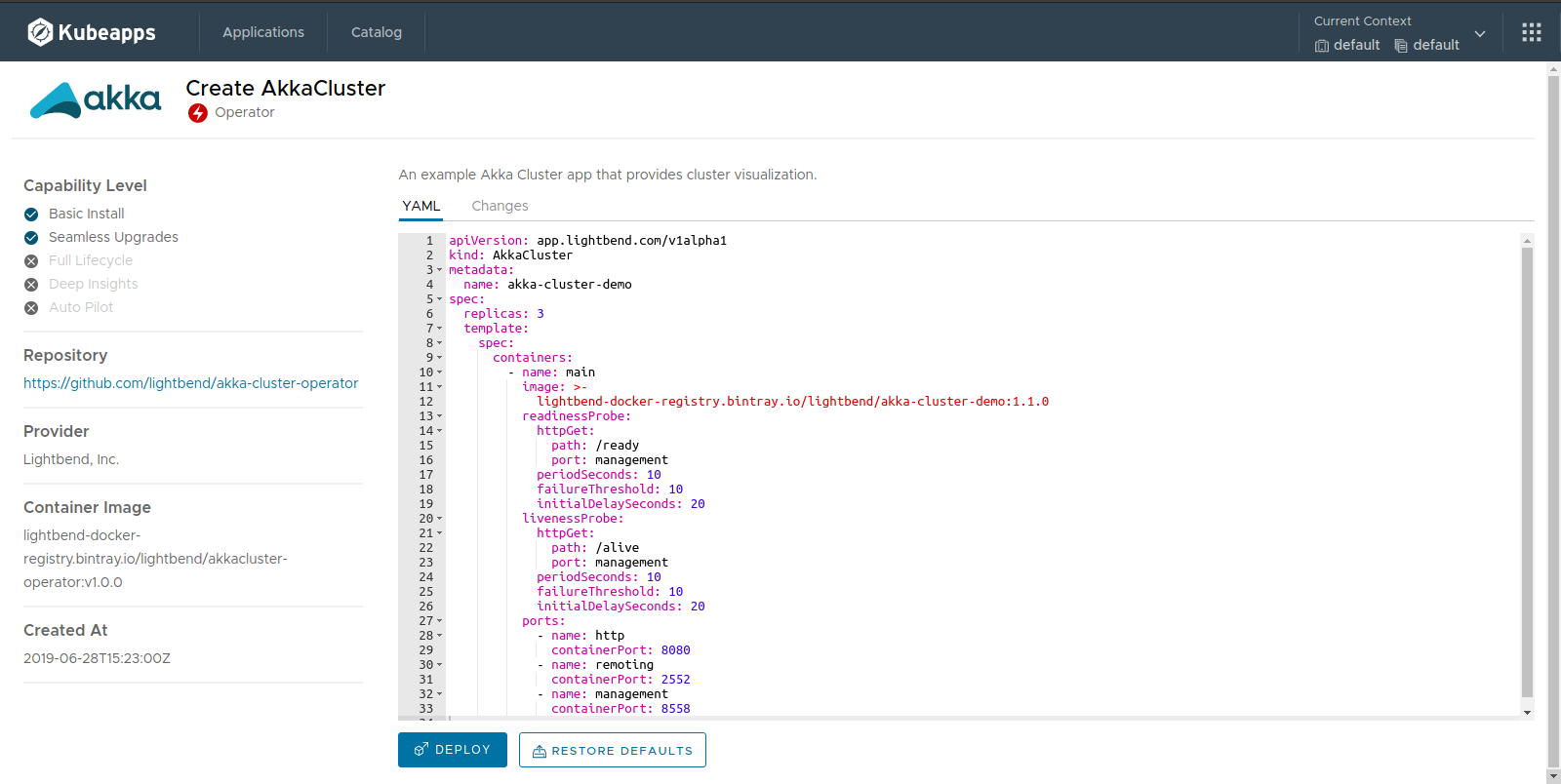
Finally, when the application or resource gets deployed, after some minutes, you will be able to inspect its status and resources:
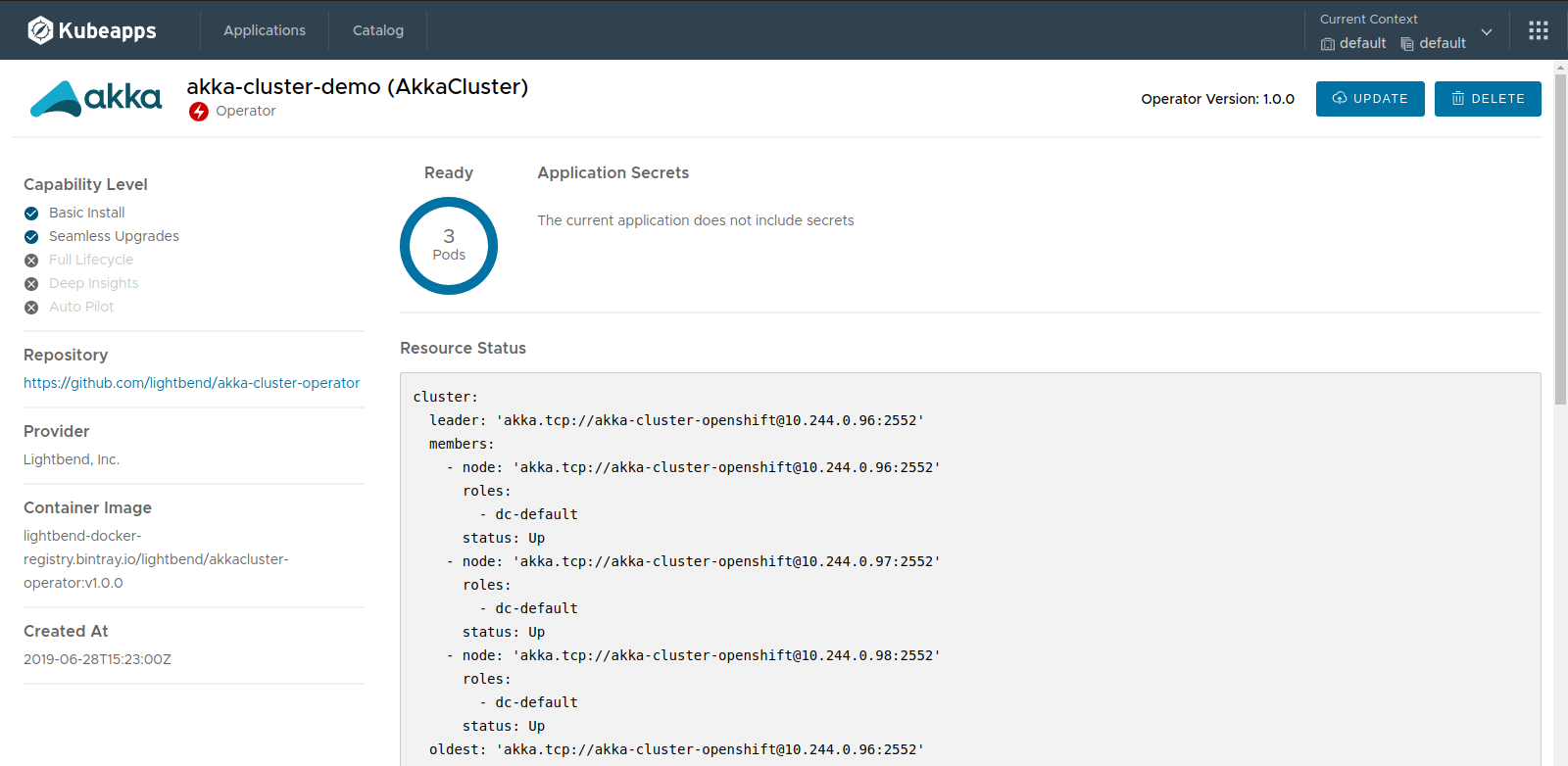
You can also click in the Update button to modify the instance or in the Delete button to remove it.
Step 5: Provide Feedback ¶
We need your feedback to improve this integration! If you find any issue or have a suggestion please open an issue in GitHub or contact us in the #kubeapps channel in Slack.

 Slack
Slack GitHub
GitHub Twitter
Twitter